What is Graves' Disease or Hyperthyroidism?
Graves' disease, or hyperthyroidism (hahy-per-thahy-roi-diz-uh m), is a condition that causes your thyroid gland to make too much thyroid hormone.
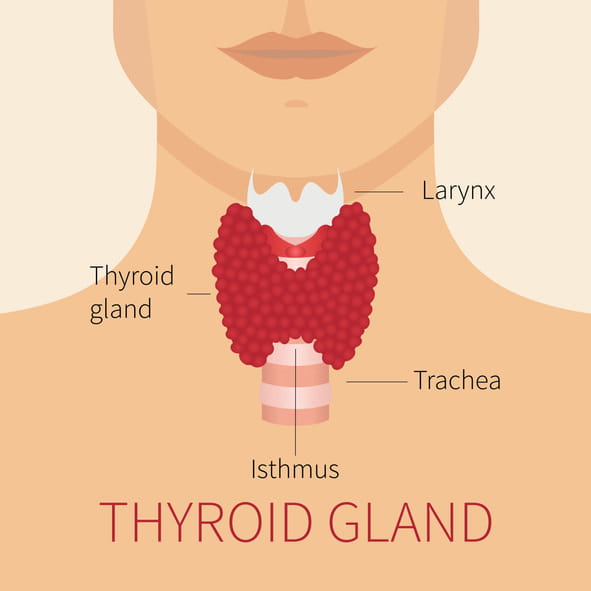
The thyroid gland is located in the neck and is shaped like a butterfly. The thyroid gland makes two important hormones: thyroxin (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3). These hormones are important for growth and development, energy, and they help the heart, liver, kidneys and skin stay healthy.
The thyroid gland is told to make T4 and T3 by another hormone, which is made in the brain. This hormone is called thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH).
Cause
The most common cause of hyperthyroidism is Graves' disease. The body’s immune system gets confused and causes the thyroid gland to make too much thyroid hormone. There are other less common causes of hyperthyroidism. Your doctor can discuss these causes with you.
Signs and Symptoms
- Increased energy (hyperactivity)
- Fatigue
- Unexplained weight loss
- Trouble sleeping
- Inability to tolerate heat
- Trouble concentrating in school
- Diarrhea
- Fast heartbeat
- Bulging eyes
- Irregular periods
- Shaking
Treatment
Hyperthyroidism can be treated by taking medication called Methimazole. This medication keeps your thyroid gland from making too much hormone. It is very important to make sure your child takes their medicine every day as instructed. Never change the medicine dose on your own.
Sometimes the medication does not work. If this happens, there are other treatments your doctor will discuss with you. Radioactive iodine (RAI) or removal of part or all of the thyroid gland with surgery are possible treatments. Your doctor will discuss the risks / benefits of these treatments with you.
Call Your Child's Doctor If:
There are several symptoms to watch for that can help your doctor treat your child with the correct dose of medication.
The dose of methimazole may be too low if your child has any of the following symptoms:
- Increased energy (hyperactivity)
- Fatigue
- Unexplained weight loss
- Trouble sleeping
- Inability to tolerate heat
- Trouble concentrating in school
- Diarrhea
- Fast heartbeat
- Bulging eyes
- Irregular periods
- Shaking
The dose of methimazole may be too high if your child has any of the following symptoms:
- Sleeping too much
- Constipation
- Cold, dry skin
- Gaining weight too quickly
- Low energy / activity level
- Abnormal menstrual cycles
Never change a medication dose on your own.
Caring for Your Child
The provider will want to see you frequently during the first year to check on your child's growth and development. Depending on your particular situation, your doctor may want to see your child as often as once a month. Blood tests during these visits will help your doctor make sure the medication dose is correct. Your provider will discuss any limits on physical activity for your child until thyroid levels improve.
It may take some time for your child to feel better. Please call your provider with concerns.