
Summary Page Total Anomalous Pulmonary Venous Return
Supracardiac TAPVC
Repaired TAPVC
Intracardiac TAPVC
Infracardiac TAPVC
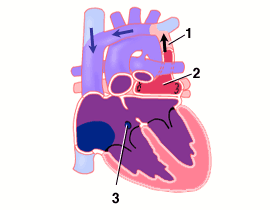
- Supracardiac-type TAPVC. Anomalous vein returning pulmonary venous blood from the lungs to the superior vena cava.
- Confluence of pulmonary veins behind, but not connected to the left atrium.
- Atrial septal defect allows blood flow to left atrium.
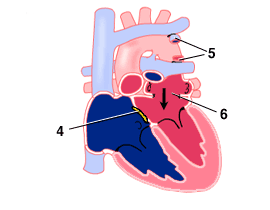
- ASD patched.
- Anomalous pulmonary venous connection divided.
- Pulmonary vein confluence attached to left atrium.
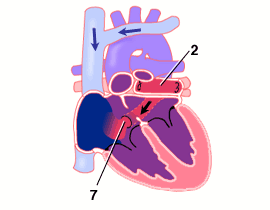
- Intracardiac-type TAPVC. Pulmonary vein confluence draining to right atrium via enlarged coronary sinus.
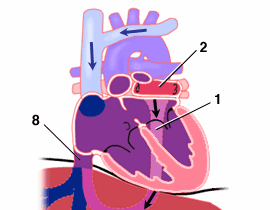
- Infracardiac-type TAPVC. Pulmonary venous blood draining through the liver to reach the IVC and right atrium.
The pulmonary veins join together in a confluence but do not attach normally to the left atrium. Instead, pulmonary venous blood is directed to the right atrium by one of three routes.
Supracardiac-type TAPVC: Blood drains from the pulmonary veins to the superior vena cava system via an anomalous "vertical vein".
Intracardiac-type TAPVC: Blood drains from the pulmonary veins to the right atrium directly via the coronary sinus, the vein that normally only drains the coronary veins of the heart muscle itself.
Infracardiac-type TAPVC: Blood drains from the pulmonary veins to the right atrium via a vertical vein that passes inferiorly through the diaphragm. This blood must then pass through the liver to reach the IVC. This pathway often causes obstruction to flow.
Repair consists of:
- Attachment of the pulmonary vein confluence to the left atrium.
- Division of the anomalous connection to the right side of the heart.
- Closure of the ASD.