Research Interests
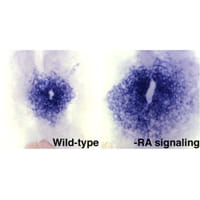
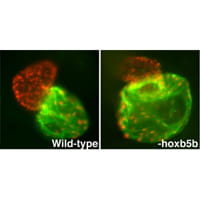
The ultimate goal of our research is to understand the mechanisms that determine organ size through selection of progenitor cells. Proper determination of organ size is crucial for normal organ form and function, and specification of organ progenitors seems to depend on a balance of inductive and restrictive signals. We currently understand much less about the signals that limit cardiac progenitor specification compared to the signals that promote cardiac progenitor formation. Therefore, our studies are focused on the signals that restrict the size of the cardiac progenitor field.