Senad Divanovic, PhD
- Director of Admissions, Immunology Graduate Program
- Associate Professor, UC Department of Pediatrics
About
Biography
My research aims to identify critical knowledge gaps that link immune responses with inflammatory, infectious and metabolic diseases. I gained expertise through the pursuit of studies arising from the reductive analysis of both innate and adaptive immune responses (e.g., TLR, BAFF, Type I IFN and IL-17 signaling) in animal models. These experiences have positioned me well to lead projects aimed at defining the mechanisms underlying immunopathogenesis of various diseases.
Research areas that interest me include immunology, immunometabolism, obesity, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and preterm birth. I began my independent research career work at Cincinnati Children's in 2010. My research has been supported by the National Institutes of Health (NIH) since 2013.
The overall goal of my research program is to define the fundamental processes, mechanisms and immune pathways underlying disease pathogenesis. My ultimate objective is translational exploitation of such insights for reducing or eliminating the burden of inflammation-associated diseases.
Specifically, the focus of my laboratory is to exploit:
- The immune pathways underlying obesity development and adipocyte-immune like behavior
- The immune pathways underling increased infectious susceptibility in obesity
- Immunopathogenesis of NAFLD
- Obesity-dependent vertical transmission of adverse offspring health outcomes
- Immunopathogenesis of preterm birth
- The role of thermoneutral housing on immune responses and disease pathogenesis
Further, our experimental models are supported by established and ever-developing platforms of primary human samples from individuals clinically stratified into respective disease categories.
Some of my most notable discoveries include identifying RP105 as a negative regulator of TLR4 signaling, demonstrating how IL-17 axis functions in the regulation of NAFLD progression and employing thermoneutrality as an improved, more “human-like” approach, to study inflammatory and metabolic diseases.
It is my honor to have received several awards, including:
- 2012 Trustee Award, Cincinnati Children’s
- 2018 Milstein Award, International Cytokine & Interferon Society (ICIS)
- 2018 Top 7 Breakthrough Discoveries, Cincinnati Children’s
- 2020 Cincinnati Children’s Research Foundation (CCRF) Endowed Scholar
- 2018 Innovative Basic Science Award, American Diabetes Association (ADA)
- 2015 Preterm Birth Initiative Award, Burroughs Wellcome Fund
BA: DePauw University, Greencastle, IN, 1998,
MS: Oklahoma State University, Stillwater, OK, 2000,
PhD: University of Cincinnati, Cincinnati, OH, 2005,
Post Doc: Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center, Cincinnati, OH, 2010,
Interests
Innate immune responses; obesity; NAFLD; preterm birth; echocardiography; fetal cardiology; Cardiology Consult Service; General Cardiology Outpatient Clinic
Research Areas
Publications
Diffuse neuroinflammation and immature neuron loss in fetal Rhesus macaques after short-term intrauterine infection. Journal of Neuroinflammation. 2026; 23(1):60.
Patient-derived colon epithelial organoids reveal lipid-related metabolic dysfunction in pediatric ulcerative colitis. Nature Communications. 2025; 16(1):11026.
Maternal metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease during pregnancy and its impact on offspring steatosis. Clinical Nutrition ESPEN. 2025; 70:327-335.
A shift in PKM2 oligomeric state instructs adipocyte inflammatory potential. JCI Insight. 2025; 10(22).
Intrauterine infection causes neuroinflammation and a selective loss of immature neurons in preterm non-human primate (NHP) fetuses 3227. Journal of Immunology. 2025; 214(Supplement_1).
Obesity Uncovers the Presence of Inflammatory Lung Macrophage Subsets With an Adipose Tissue Transcriptomic Signature in Influenza Virus Infection. Journal of Infectious Diseases. 2025; 231(2):e317-e327.
Knockdown of ketohexokinase versus inhibition of its kinase activity exert divergent effects on fructose metabolism. JCI Insight. 2024; 9(23).
STARD7 maintains intestinal epithelial mitochondria architecture, barrier integrity, and protection from colitis. JCI Insight. 2024; 9(22).
Azathioprine promotes intestinal epithelial cell differentiation into Paneth cells and alleviates ileal Crohn's disease severity. Scientific Reports. 2024; 14(1):12879.
Presurgery health influences outcomes following vertical sleeve gastrectomy in adolescents. Obesity. 2024; 32(6):1187-1197.
From the Blog
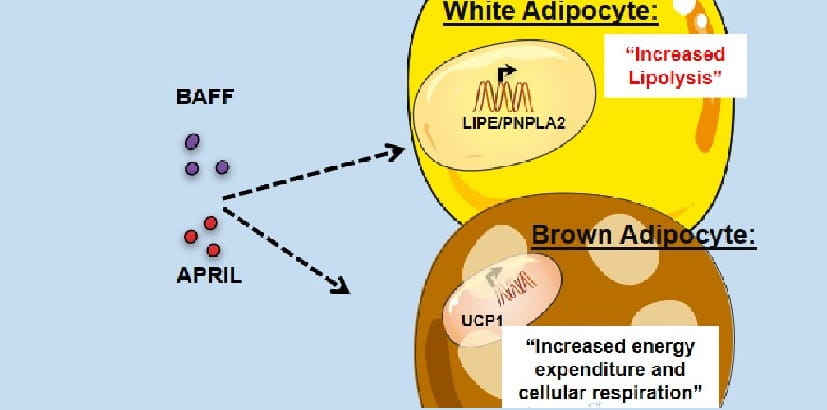
Study reveals potential new way to burn fat faster
Senad Divanovic, PhD5/18/2021
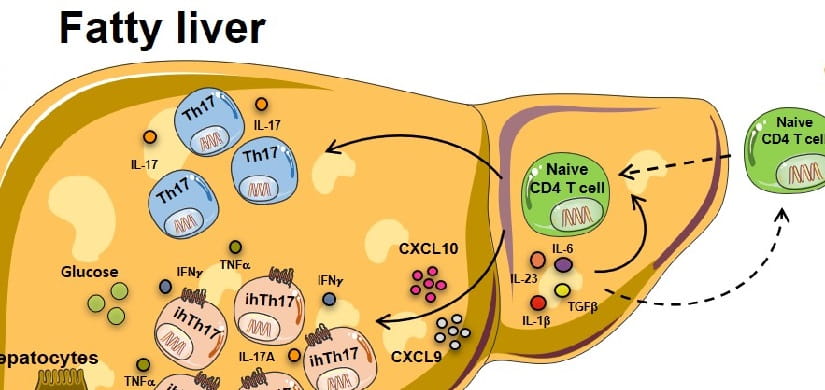
Research Reveals Potential Treatment to Prevent Obesity-Driven Liver Damage
Senad Divanovic, PhD5/17/2021
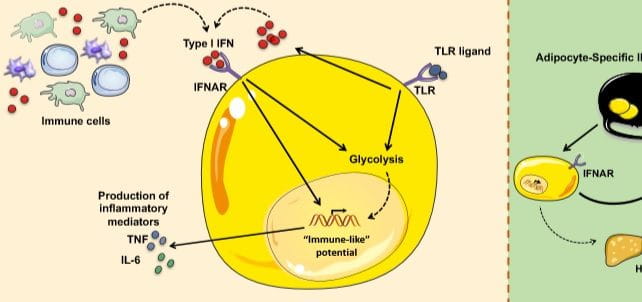
How a Fat Cell’s Immune Response Makes Obesity Worse
Senad Divanovic, PhD6/2/2020
‘Thermoneutral’ Mouse Model Opens Doors for Obesity Research
Senad Divanovic, PhD7/3/2019