Interstitial, Rare-lung Diseases, and Transplantation
Xenon-129 Gas and Magnetic Resonance Imaging use in Transplantation
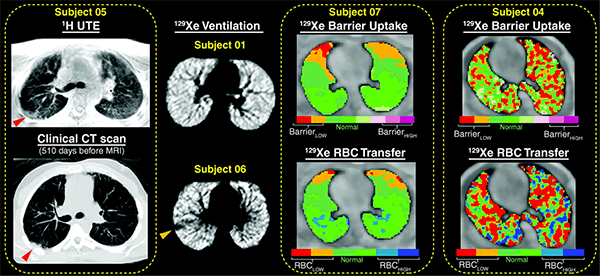
Early detection of pulmonary morbidity following hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) is an important challenge for intervention, mainly due to the insensitivity of spirometry to early change. In the pediatric population, patient compliance provides additional challenges. In our research efforts we have quantified regional lung ventilation abnormalities in pediatric HSCT patients using hyperpolarized xenon-129 (129Xe) magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) compared to the traditional method of spirometry.
Imaging in other Diseases and Transplantation
Pulmonary complications following allogeneic HSCT are a major source of morbidity and mortality. These complications may arise early or later post-transplantation and may stem from bacterial or fungal infections or from non-infectious sources such as pulmonary edema or drug-related toxicity related to immunosuppression and chemotherapy.
Our current studies focus on hematopoietic stem-cell transplantation (HSCT), interstitial lung disease (ILD), bronchiolitis obliterans (BOS) and primary ciliary dyskinesia (PCD).