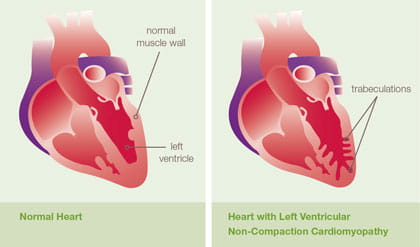
What is Left Ventricular Non-Compaction Cardiomyopathy (LVNC)?
In left ventricular non-compaction cardiomyopathy (LVNC) the lower left chamber of the heart, called the left ventricle, contains bundles or pieces of muscle that extend into the chamber. These pieces of muscles are called trabeculations. During development, the heart muscle is a sponge-like network of muscle fibers.
As normal development progresses, the trabeculations become compacted transforming the heart muscle from sponge-like to smooth and solid. LVNC occurs when compaction does not occur. These trabeculations typically occur at the bottom of the heart called the apex but can be seen anywhere in the left ventricle. Individuals with LVNC may also have another type of heart muscle disease (hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, dilated cardiomyopathy or restrictive cardiomyopathy).
LVNC is being diagnosed more frequently in both children and adults secondary to increased awareness of the condition. The initial diagnosis may be made at any age and many patients often go undiagnosed until later in life.